Thus the increasing number of nucleus attracts the more electrons more tightly towards it and the atomic radius decreases. This is due to the presence of fully filled 2s.
The Size Of Atom Decreases Across A Period From Left To Right Description From Streamscience Blogspot Ionization Energy Chemistry Chemistry Periodic Table
Department of Energy has estimated that after five years there were perhaps 200000 or more fatalities as a result of the bombing while the city of.
. First ionisation energy down group 2. It is very easy to remove an electron from an atom that is very far from an octet. First ionisation energy across period 3.
Electronegativity down group 2. Periodicity of Valence or Oxidation States. Justify the given statement with suitable examples the Properties of the elements are a.
So removing an electron becomes harder and harder and the ionization energy increases as atoms approach an octet. The first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period. Atomic Radius Trend 1.
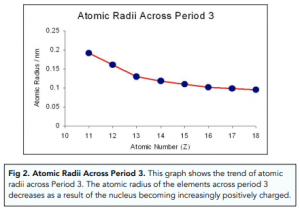
Atomic Radii Decrease From Left to Right Across a Period. Atomic radius across period 3. This is because the effective positive force of the nucleus also increases drawing in the electrons more tightly.
Atomic radius decreases across the period. Periodic Trends and Chemical Reactivity. This is because the starting elements in a period tend to form cations and the elements.
Electronegativity across period 3. Trends in Ionic Radius Across a Period. The atomic radius decreases as we move towards periods and increases as we go down the group.
In 1913 chemistry and physics were topsy-turvy. Meanwhile the total organic carbon removal increased from 0029 mg L 1 to 1273 mg L 1 with the applied potential increased from -06 to -12 V vs. Between 90000 and 166000 people are believed to have died from the bomb in the four-month period following the explosion.
Moreover the intensity profiles along with the direction of XY in Fig. Ionic Radii - It is the distance between the nucleus and the electron in the outermost shell of an ion. During the Second World War Britain.
Atomic radius down group 2. The ionisation energy on the other hand increases across the period from left to right because of a decrease in atomic size from left to right. Atomic radius increases down the group.
How Many Times Class 3 Notes CBSE Maths. In general as atomic size increases the ionisation energy decreases down the group. Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements.
This increased nuclear charge attracts the electrons more strongly to the nucleus making the. For example Sodium in period 3 has an atomic radius of 186 picometers and chlorine in the same period has an atomic radius of 99 picometers. Melting and boiling points across period 3.
As we move from left to right across a period the ionization enthalpy keeps on increasing due to increased nuclear charge and simultaneous decrease in atomic radius. For example magnesium atomic weight 243 is placed to the right of sodium atomic weight 230. Electrical conductivity across period 3.
Even though each atom has more electrons as you move from left to right across the periodic table the atomic radius decreases. Let us understand the trends in the ionic radius of elements across a period with an example. In period 3 we find that the atomic radius first decreases and then suddenly increases and then again it slowly decreases.
A higher atomic weight than the one on its left. Upon additional CV scans the intensity of PdH 3 O 2 exhibited changes in period showing that the formation of PdH 3 O 2 can be readily tuned by changing the applied potential Fig. The first atomic bomb Little Boy was dropped on Japan on August 6 1945.
In atomic physics the Bohr model or RutherfordBohr model presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913 is a system consisting of a small dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electronssimilar to the structure of the Solar System but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces in place of gravityIt came after the solar system Joseph Larmor model. As you move from left to right across an element period row the ionic radius decreases. Even though the size of the atomic nucleus increases with larger atomic numbers moving across a period the ionic and atomic radius decreases.
Some big hitters - including Mendeleev - were talking seriously about elements lighter than hydrogen and. Trends in Physical Properties Atomic Radius Ionic Radius Ionisation Enthalpy Electron Gain Enthalpy Electronegativity Periodic Trends in Chemical Properties. The True Basis of the Periodic Table.
1b uncover that the smallest separated distance of Ru atoms is at least ca. Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 3 Genesis of Periodic Classification Dobereiners Triads In 1829 Dobereiner arranged certain elements with similar properties in groups of three in such a way that the atomic mass of the middle element was nearly the same as the average atomic masses of. Operation Hurricane was the first test of a British atomic deviceA plutonium implosion device was detonated on 3 October 1952 in Main Bay Trimouille Island in the Montebello Islands in Western AustraliaWith the success of Operation Hurricane Britain became the third nuclear power after the United States and the Soviet Union.
Moving from left to right across a period the number of protons and electrons increases while the number of energy shells stay same. It follows the same trend as that of the atomic radii increases as we go down the group and increases as we move across a period. When an electron is added a new proton is also added to the nucleus which gives the nucleus a.
However there are some exceptions given below- In spite of increased nuclear charge the first ionisation enthalpy of B is lower than that of Be. 1c exceeding the Ru-effective. Melting and boiling points down group 2.
Within a period of elements each new electron is added to the same shell. A group 1 element that has one valence electron will readily lose its. This is because Chlorine has a larger number of protons and a higher nuclear charge with no additional shells to put the electrons further away.
Ionic radius also decreases although not for the exact same reason. AgAgCl Zeng et al 2020c. The reason is that youre also adding more protons which exert a stronger attractive force on the electrons drawing them in a tiny bit closer.
As elements have successively more electrons across a period atoms get closer and closer to their goal.
Periodic Trends And Atomic Radius Chad S Prep
Atomic Radius Definition Determination Chart Trend In Periodic Table
Periodic Trends In Electronegativity Ck 12 Foundation Chemistry Periodic Table Ionization Energy Teaching Chemistry
Atomic Radius Trends On Periodic Table Video Khan Academy
Periodicity Trends Along Period 3 A Level Chemistry Study Mind
The Periodic Properties Of The Elements Teaching Chemistry Science Chemistry Science Notes
Periodic Trends Variation In Atomic Radii Of Elements In Different Blocks Chemistry Stack Exchange
Suka Chemistry Atomic Radius Trends On Periodic Table
The Periodic Table Is Called This Not Just Because It Is A Table Of The Elements But Because It Is Arranged Ionization Energy Study Biology Electron Affinity
Atomic Radius Trend Periodic Table Chemtalk
Periodic Trends In Atomic Size Ck 12 Foundation
Periodicity Definition In Chemistry Electron Affinity Ionization Energy Chemistry
Periodic Trends In Ionic Radii Chemwiki Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Element Chemistry
Trends In The Periodic Table Chpt 7 1 Atomic Radius Size 2 Ionization Energy 3 Electronegativity The Ionization Energy Periodic Table Covalent Bonding
Periodic Trends Definition And Properties
Atomic Radius Definition Formula Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic Radii Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity Socratic
- cara buat laporan
- chord gitar surat cinta
- karikatur hitam putih mudah
- contoh frasa dengan kata nama am
- cara buat almond london
- owner in malay
- pembekal tanah merah di klang
- poskod sungai udang melaka
- baby berak berdarah
- undefined
- atomic radius across period 3
- taman raub jaya 3
- al quran online malaysia
- khat kufi allah
- jenis ikan baung di malaysia
- range rover price malaysia
- daun pandan rice dumpling outlets
- cyberia crescent 2
- bahagian teknologi pendidikan negeri pulau pinang
- maybank go ahead challenge
